What is Wet Bulb Globe Temperature?
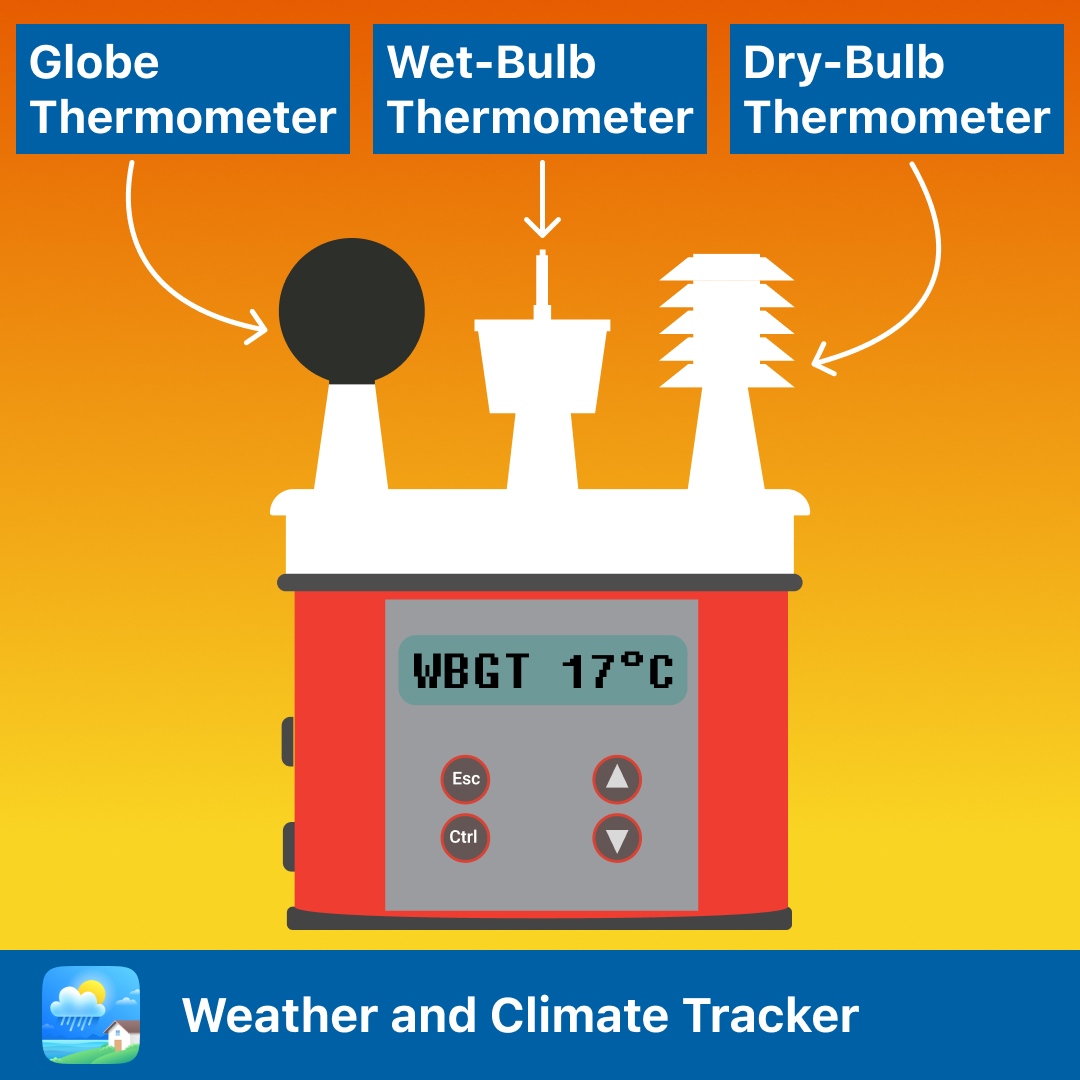
In order keep safe when it’s hot outside, it’s important to know how hot it really feels. Scientists created something called the Wet Bulb Globe Temperature or WBGT to measure the heat stress in the air.
Imagine you have three thermometers: a regular one, a wet one, and one inside a shiny black ball. The regular thermometer just reads the temperature in the air. The wet one has a cloth cover, so water evaporates off it and cools it down. That measures how humid the air is. The globe thermometer inside the shiny sphere heats up in the sun, just like your skin does.
By measuring all three at once - the air temp, humidity and solar heating - scientists can work out the WBGT. That tells you how your body will experience the heat - whether it will feel hot and uncomfortable, or even dangerous if you stay outside for long. On a hot, humid, sunny day, the Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) will be higher than a cooler, less humid day with some shade.
We use the WBGT measurement to decide if it’s safe to stay long outside. When the Wet Bulb Globe Temperature (WBGT) gets too high, it can be dangerous and cause heat illnesses. So stay hydrated, take breaks in the shade and limit your time outside on very hot days!
So stay hydrated, take breaks in the shade and limit your time outside on very hot days!
This post is also available in: Spanish, Russian, Ukranian, Belarusian, Portuguese, French, Turkish.



