[Sky]
Leonid Meteor Shower
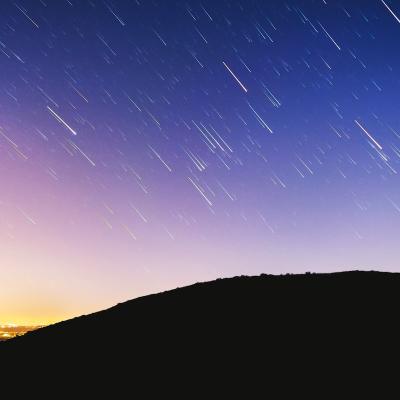
The Leonid Meteor Shower is an annual celestial event awaited by stargazers. The Leonid Meteor Shower is named after the constellation Leo, from where the meteors appear to emanate. It occurs when Earth crosses the debris trail left by comet 55P/Tempel-Tuttle. This event is known for its bright meteors and persistent trails left in the sky, providing a spectacular view for observers.
Read more...